链表数据结构
2021-05-19 22:05:34 大约 2 分钟
链表存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个 元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成。下图展示了链表的结构:
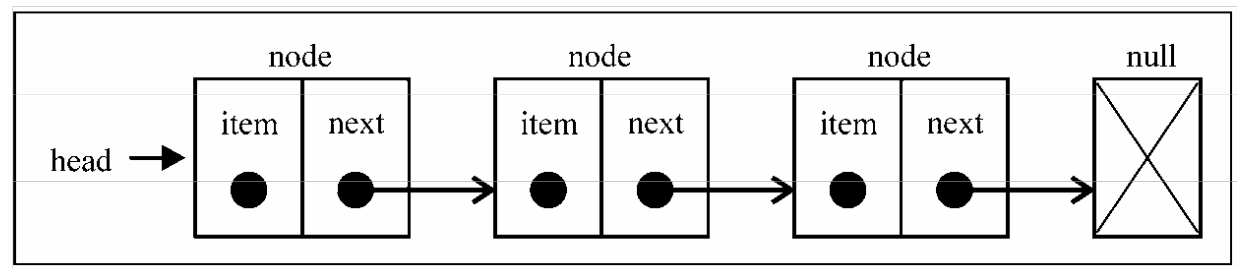
相对于传统的数组,链表的一个好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素。然而,链表需要使用指针,因此实现链表时需要额外注意。 数组的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何位置的任何元素,而要想访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点(表头)开始迭代列表直到找到所需的元素
# 普通链表
// 链表节点
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
// 链表类
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
// 用来表示节点的长度;
this.length = 0;
}
// 追加元素
append(element) {
let node = new Node(element);
// 存储下一个数据的引用;
let current = null;
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// 追加到最后一个链表的next上;
current.next = node;
}
this.length++;
}
// 任意位置插入元素
insert (position, element) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
let index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true
}
return false
}
// 移除指定位置元素
removeAt(position) {
if (position > -1 && position < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
let previous = null;
let index = 0;
if (position === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
} else {
while(index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
return null
}
// 寻找元素下标
findIndex(element) {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current) {
if (element === current.element) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
// 删除指定文档
remove(element) {
let index = this.findIndex(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
isEmpty() {
return !this.length;
}
size() {
return this.length;
}
// 返回所有链表的值
toString() {
let current = this.head;
let arr = [];
while (current) {
arr.push(current.element);
current = current.next;
}
return arr;
}
}
const ll = new LinkedList();
ll.append(2);
ll.append(4);
ll.append(6);
ll.append(8);
ll.append(10);
ll.removeAt(0);
console.log(ll.remove(10)) // 10
console.log(ll.findIndex(6)) // 1
console.log(ll.toString()); // [ 4, 6, 8 ]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
遍历链表:
function traversal(linkedList, callback) {
let current = linkedList.head || {};
callback(current.element)
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
callback(current.element)
}
}
let sum = 0
traversal(ll, (value) => sum += value)
console.log(sum) // 18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 环行链表
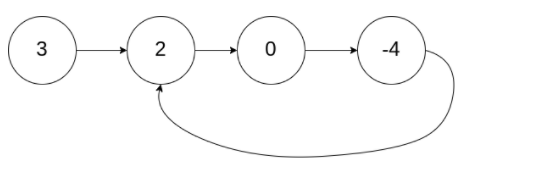
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode) 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle
const head = {
value: 1,
next: null
}
var hasCycle = function(head) {
// 快慢指针
let fast = head
let slow = head
while(fast && fast.next){
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if(fast === slow){
return true
}
}
return false
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
解题思路:让xxx.next.next和xxx.next一直比较是否相等,如果相等则存在环;
