vuex源码实现
2021-08-30 21:25:23 大约 4 分钟
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。组件树构成了一个巨大的“视图”,不管在树的哪个位置,任何组件都能获取状态或者触发行为!
# 基本使用
安装:
yarn add vuex1引入vuex插件
store/index.jsimport Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) export default new Vuex.Store({...})1
2
3
4
5
6在根示例上添加该实例:
main.js:import store from './store' new Vue({ store, render: h => h(App), }).$mount('#app')1
2
3
4
5使用:
export default new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: '' }, mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++; } } })1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<template> <div id="app"> <button @click="click">点击</button> {{ $store.state.count }} </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', methods: { click() { this.$store.commit('increment') } } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 自己的vuex
仿着vuex的基本功能实现一个自己的vuex;vuex基本使用的方式不变,我们简单实现下vuex内部的代码;
新建vuex/index.js,添加Store类和install方法并导出;
let Vue = null;
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// 因为vue中的data是响应式的,所以我们可以直接new Vue();
this.state = new Vue({
data: options.state,
})
}
}
function install (_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
// 访问到根组件时,将其挂载到vue的原型链上;
if (this.$options.store) {
Vue.prototype.$store = this.$options.store;
}
}
})
}
export default {
Store,
install
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
以上的实现代码,可以满足基本使用中count的访问,但是commit还不能使用。
# 实现commit
class Store {
constructor(options) {
+ this._mutations = options.mutations,
this.state = new Vue({
data: options.state,
})
}
+ commit(type, palyload) {
+ const enter = this._mutations[type];
+ if (enter) {
+ enter(this.state, palyload);
+ }
+ }
+}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
以上的实现代码,可以满足基本使用中count的设置了,
this.$store.commit('increment')。
# 实现dispatch
let Vue = null;
class Store {
constructor(options) {
this._mutations = options.mutations;
+ this._actions = options.actions;
this.state = new Vue({
data: options.state,
})
// 解决this指向问题
+ this.commit = this.commit.bind(this);
+ this.dispatch = this.commit.bind(this);
}
...省略中间代码
+ dispatch(type, payload) {
+ const enter = this._actions[type];
+ if (enter) {
+ enter(this, payload)
+ }
+ }
+}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
以上的实现代码,你可以
this.$store.dispatch('increment'),来使用了。
# 实现getter
vuex的getter其实就是计算属性,所以实现getter就是实现vue的计算属性;
let Vue = null;
class Store {
constructor(options) {
this._mutations = options.mutations;
this._actions = options.actions;
+ this._wapperdGetters = options.getters;
+ this.getters = {};
// 初始化 state
+ this.initVm(options);
this.commit = this.commit.bind(this);
this.dispatch = this.dispatch.bind(this);
}
initVm(options) {
const computed = {};
Object.keys(this._wapperdGetters).forEach(key => {
// 获取用户定义的getter;
const fn = this._wapperdGetters[key];
computed[key] = () => {
return fn(this.state)
}
// 定义只读
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, key, {
get: () => {
return this._vm[key]
}
})
})
this._vm = new Vue({
data: options.state,
computed,
})
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
以上的实现代码,你可以
this.$store.getter.xxx,来使用了。
# 禁止直接修改state
以上的代码实现简单实现了vuex的基本功能,但是用户还可以直接
this.$store.state = xxx来修改,这样是不应该的,所以我们需要限制用户直接修改state中的值;
class Store {
+ get state () {
// 需要this._vm._data访问
+ return this._vm._data.$$state;
+ }
+ set state (v) {
+ console.error('禁止直接修改state')
+ }
initVm(options) {
this._vm = new Vue({
data: {
+ $$state: options.state,
},
computed,
})
}
+}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# 完整代码
let Vue = null;
class Store {
constructor(options) {
this._mutations = options.mutations;
this._actions = options.actions;
this._wapperdGetters = options.getters;
this.getters = {};
// 初始化 state
this.initVm(options);
this.commit = this.commit.bind(this);
this.dispatch = this.dispatch.bind(this);
}
get state () {
return this._vm._data.$$state;
}
set state (v) {
console.error('禁止直接修改state')
}
initVm(options) {
const computed = {};
Object.keys(this._wapperdGetters).forEach(key => {
// 获取用户定义的getter;
const fn = this._wapperdGetters[key];
computed[key] = () => {
return fn(this.state)
}
// 定义只读
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, key, {
get: () => {
return this._vm[key]
}
})
})
this._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: options.state,
},
computed,
})
}
commit(type, palyload) {
const enter = this._mutations[type];
if (enter) {
enter(this.state, palyload);
}
}
dispatch(type, payload) {
const enter = this._actions[type];
if (enter) {
enter(this, payload)
}
}
}
function install (_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.store) {
Vue.prototype.$store = this.$options.store;
}
}
})
}
export default {
Store,
install
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
以上就是vuex的核心内容了,但是只是一个简单的vuex,主要用于学习目的;
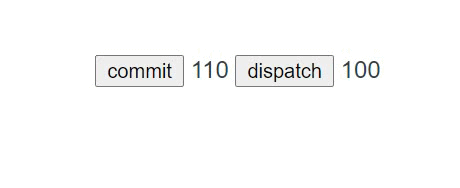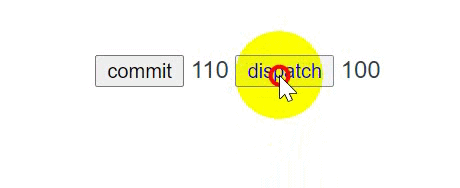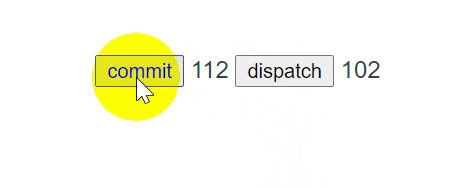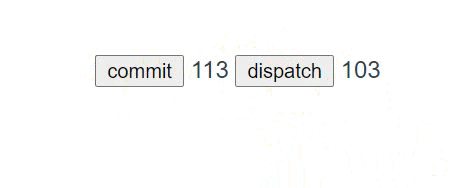
# 测试
import Vue from 'vue';
// 引入自己写的vuex
import Vuex from '../plugin/vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 100
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++;
}
},
actions: {
increment({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
},
getters: {
num(state){
return state.count + 10;
}
}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="click">commit</button>
{{ $store.getters.num }}
<button @click="onclick">dispatch</button>
{{ $store.state.count }}<br>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
click() {
this.$store.commit('increment')
},
onclick() {
this.$store.dispatch('increment')
}
}
}
</script>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21